Hair Loss After Sleeve Gastric Surgery
One of the most common problems after sleeve gastric surgery is hair loss. The hair loss usually occurs between third and ninth month after sleeve gastric surgery. In fact, this is temporal and is not a health problem. However, when the appearance and psychological factors are considered, hair loss requires an intervention.
A small amount of hair loss is a common problem that lasts three or more months after sleeve gastric surgery and affects nearly one-third of the patients. The exact reasons for hair loss are not entirely clear. But it is believed that bariatric surgery leads to changes in nutritional status and dietary restrictions, so it affects the hair growth cycle. After stabilizing weight, new hair growth occurs with no intervention.
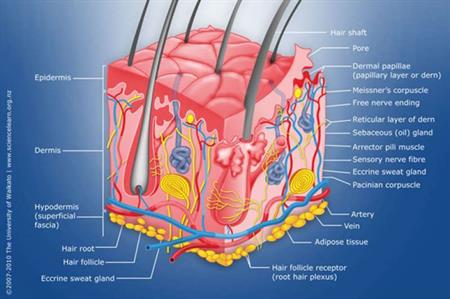
Structure of Human Hair
Human hair is made up mainly of protein (keratin). It also contains lipids (fats and oils), water, pigments, and trace amount elements. You can see the anatomical structure and parts of the hair in the picture below.
Hair Growth Cycle
Hair growth occurs in the typically three-phases cycle as follows:
- Anagen Phase: During the Anagen or growth phase, cell division in the papilla causes the lengthening hair shaft and the new growth occurs from the root of hair to the upward. The Anagen phase may last between 2 and 10 years, but mostly lasts generally between 3 and 5 years. During this time, the hair grows about 1-1,5 cm. This rate of time and growth can be influenced by genetic, hormonal, and metabolic factors. It can also show sensitization to seasonal changes. Typically between 80% and 90% of hair is in the Anagen phase at any given time. At the end of the Anagen phase, the hair enters a transition period called Catagen phase.
- Catagen Phase: Mitotic division stops in Catagen phase. The hair follicle contracts and its food source cut out of the root (papilla). The formation of the medulla and cuticle ends. This phase lasts between 1 and 2 weeks. Only 1% of your hair is in this phase at any time.
- Telogen Phase: The Telogen phase is a stagnation phase. The hair follicle stagnates for 1-4 years before Anagen phase starts again. The old hair is pushed down from the follicle as new hair grows in the roots.
There are nearly 100,000 hairs in a healthy human scalp and 100 of them are lost in every day.
How to Diagnose Hair Loss
Hair loss usually occurs in 3-6 months after bariatric, but this period may sometimes be longer due to various reasons. The diagnosis usually made through medical history and clinical examination; there are some signs such as significantly increased hair loss, associated symptoms such as skin and nail abnormalities, and caused by taking some medicines. There are some tests can be done if there is any doubt about the type or cause of hair loss. If necessary, hair follicles can be taken for microscopic examination and to examine malnutrition, hormonal imbalances, and other diseases, some blood tests can be done.
Subtypes of Hair Loss
- Telogen Effluvium: Since most of the hair is in the Anagen (growth) phase, daily hair loss after Telogen (hair loss) phase usually does not draw the attention. This type of hair loss does not generally cause bald spots on the head, but the hair becomes thinner.
This often leads to hair loss in situations where there are potential triggers such as surgery, childbearing, rapid weight loss, taking medicine, hormonal changes, chronic diseases, hypothyroidism, malnutrition, and physiological or psychological stress. Surgical procedures that require anesthesia are particularly associated with Telogen Effluvium. Anesthesia can lead some anagen (growth) hair follicles to be move to the premature Telogen (early hair loss) phase by blocking the rapid cell division needed to maintain hair growth. Telogen phase may last a few months; also it usually creates a delay between the triggering event and hair loss.
- Alopecia Areata (Bald Spots): This is a chronic condition that recurring hair loss for some unknown reasons. It is generally known bald spots.
- Androgenetic Alopecia: It is also known as a male bald head. This type of hair loss is seen more often in men than women. Increased androgen levels in the papilla may shorten Anagen until the follicle completely stops hair growth; it also reduces the shaft diameter, length, and pigmentation of the hair. Androgenetic Alopecia is inherited. Also, it is related to metabolic conditions such as insulin resistance, polycystic ovary syndrome, and diabetes.
Hair Loss Because of Malnutrition
Hair loss lasts longer than 6 months after bariatric surgery or if it occurs after 12 months of the surgery, the malnutrition is suspected. Although rapid weight loss is a known trigger for Telogen Effluvium type of hair loss, some food deficiencies may also cause hair loss. Hair loss due to the malnutrition usually occurs in conditions such as skin, nail abnormalities etc.
- Zinc
Zinc is one of the essential minerals that the human body needs it. Zinc deficiency is due to malnutrition or malabsorption. Hair loss, weakness of the immune system, late healing of wound, and skin lesions can occur in zinc deficiency.
It also regulates the signaling pathway which controls the transition from Telogen (stagnation) to Anagen (growth). Zinc deficiency is related to Telogen Effluvium and Alopecia Areata; white, thin, and weak hairs may grow in its deficiency. It is also related to diabetes, sickle cell anemia, and some other chronic diseases. Zinc plays an important role on the movement of prostate gland, the work of reproductive organs, and increasing of the sperm motility. It is involved in the metabolism of thyroid hormones.
The bariatric surgery is a risk factor for zinc deficiency. In particular, some gastrointestinal alterations and procedures, such as gastric bypass, ileal interposition, and transit bipartition, can reduce zinc absorption. After operations like sleeve gastric surgery, zinc deficiency may occur because of malnutrition.
Zinc supplement should not be used without doctor’s advice and supervision. Especially some supplements which are very popular recently should not be used without medical and specialist advice. Excessive zinc consumption can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomachache.
The recommended daily amount of zinc is between 11 and 15 mg.
- Iron
The main function of iron in the body is to participate in red blood cells, which are transporting oxygen from the lungs to all other organs. Iron deficiency reduces the amount of hemoglobin in the blood; it is defined as iron deficiency anemia.
Malnutrition, malabsorption, gastrointestinal bleeding, menopause, pregnancy, and menstruation can cause iron deficiency.
Malabsorptive operations can lead to reduced iron absorption. Also, insufficient iron intake can occur due to the restrictive surgeries (such as sleeve gastrectomy, gastric folds, etc.) that cause malnutrition.
Iron deficiency anemia may show some indications such as tachycardia (heart rhythm disorder), tiredness, and shortness of breath. Low iron levels, even if they are less than anemia levels, can lead to a keratin disorder in the hair structure, so it is possibly associated with Telogen Effluvium, Alopecia Areata, and Androgenetic Alopecia. However, there are different data on this subject and there is no consensus about the role of iron in hair loss.
- Biotin
Biotin is one of the B-complex vitamins. It is also known as B7 and H vitamins. Biotin is good for fat and protein metabolism. It also supports both converting carbohydrates to glucose and feeding skin, hair and nails. Water soluble vitamin B7 cannot be stored in the body, but it is taken from various foods and it can be produced by the intestinal flora.
Biotin deficiency is extremely rare. Anti-epileptic drugs and malabsorption conditions such as Crohn's disease, and long-term parenteral nutrition (intravenous feeding) may cause the biotin deficiency.
Recent studies have shown that post-bariatric hair loss reduced in people who take supplements. However, there is no relation between bariatric surgery and biotin deficiency.
- Protein
Fundamental constituents of proteins and human body are amino acids. While some amino acids can be synthesized in the human body, the others (essentials) must be taken through foods.
Proteins taken through foods are broken down by the digestive tract, and it is provided that amino acids necessary for tissue growth are attained.
The keratin in the hair structure is protein. Protein malnutrition (especially L-Lysine) can affect hair growth. After inadequate protein intake, hair loss can occur related to Telogen Effluvium. Also, there may be hair loss and loss of elasticity and discoloration in hair.
In addition, there may be hair loss, loss of elasticity, thinning, discoloration, discoloration from brown hair to yellow hair, red and yellow streaks in dark hair.
- Essential Fatty Acids
Linoleic acid from the Omega-6 group and α-Linoleic acid from the Omega-3 group are some essential fatty acids that are important for human health. These fatty acids cannot be synthesized in the human body. So, nutrients like flaxseed, leafy vegetables, seafood, etc. must be taken.
Essential fatty acids deficiency can occur after the gastrointestinal operations (such as gastric bypass and ileal interposition) that affect lipid metabolism. Skin lesions, hair pigmentation, scalp flaking, and eyebrow loss are some indications in association with fatty acid deficiency.
- Copper
Copper is one of the trace elements in the human body. Copper is involved in various metabolic processes in the central nervous system and brain; also it is necessary for the immune system, creation of connective tissue and production of melanin. Copper deficiency is rarely observed. It might be occurred only after malabsorptive operations.
Copper deficiency can cause neurological problems such as gait abnormalities, loss of perception, visual disturbances, visual disturbances, and etc. Copper plays an important role in iron absorption, so it can lead to hair loss associated with iron deficiency.
- Other Nutrients
Vitamin B3 (Niacin), Vitamin B12, Selenium, Vitamin A, Vitamin C, and other micronutrient deficiencies are some deficiencies that can occur after bariatric surgery due to malnutrition. These nutrients can be associated with hair loss and hair growth.
Control of Hair Loss After Bariatric Surgery
Hair loss after bariatric surgery is usually temporary, but the precautions may be needed to reduce hair loss. In most cases, the hair grows back within a few months (first 9 months) after rapid weight lost period. If the hair loss continues for 6 months or more, other causes of the hair loss are examined and the hair loss is tried to be slowed down.
Food Supplements Are Not A Solution!
Given the specific nutrient deficiencies associated with hair loss, these nutrients are effective for growing the hair, but it is not proven that this prevents or treats hair lost after bariatric surgery. Many scientific studies on hair loss show that whether iron, zinc and biotin supplements or zinc shampoo, micro supplements, topical preparations did not prevent hair loss and substantially succeed.
Taking too many water-soluble vitamins, such as biotin, does not benefit for hair loss, but it is not injurious to health taking them as a supplement. However, excessive consumption of elements such as iron, zinc or copper can cause toxic effects. With doctor’s advice and supervision, taking adequate nutrition, bariatric diet and supplementary foods reduce the risk of hair loss and they are good for your general health.
Should I use Minoxidil?
Rocaine, Regain or Loniten can be used for hair growth. In the 1970s, Minoxidil was used for the treatment of high blood pressure, but it was withdrawn from the market because it caused hirsutism. Minoxidil is believed to stimulate hair growth by extending the Anagen cycle and increasing blood flow to the hair follicles. Minoxidil can be used for the topical treatment of Alopecia Areata (male pattern baldness). Stopping the use of Minoxidil causes the hair loss to start again. Some people have reported that hair loss increased after taking Minoxidil. It is shown that in the treatment of Telogen Effluvium that using Minoxidil lead to hair growth, but this has not been proven.
Finasteride
Androgenic alopecia is a medication that taken by orally and it is used by men. It is considered equivalent to topical Minoxidil. It may cause loss of sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, and male breast cancer.
Hair Transplantation
In some cases, permanent hair loss may require intervention like hair transplantation. After bariatric surgery, it is necessary to stabilize hair growth time to think about hair transplantation. Therefore, it is recommended to wait at least two years after the operation.
Biochemist
Alper Habip
References
1. Gordana Bosnic, Critical Care Nursing Clinics of North America, Volume 26, Issue 2, Pages 255-262, June 2014.
2. Amanda Velazquez, Caroline M. Apovian, Nawfal W. Istfan, The American Journal of Medicine, Volume 130, Issue 7, Pages e293-e294, July 2017.
3. Dimitris Papamargaritis, Erlend T. Aasheim, Barry Sampson, Carel W. le Roux, Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology, Volume 31, Pages 167-172, July 2015.
4. Meyler's Side Effects of Drugs (Sixteenth Edition), Minoxidil, Pages 1053-1056, 2016.